Switching to electronic invoices certainly brings a revolution to businesses in Malaysia. Of course, understanding the e-invoicing process is important as Malaysia moves towards making it mandatory, starting August 2024.
This process involves the exchange of e-invoices between suppliers and buyers, eliminating the need for traditional paperwork. If you don't grasp e-invoicing digital transformation, you will have difficulty setting it up and putting it into operation in your business.
Read our article to discover detailed steps on how does e-invoicing works and to make this journey a smooth one for your business!
How Does E-Invoicing Work: 3 Needed Parts To Be Known
Understanding how does e-invoicing work, first, includes grasping the three needed parts: e-invoicing addresses, formats, and infrastructure. Each part plays an important role in ensuring the smooth operation of e-invoicing.
E-Invoicing Addresses
To engage in e-invoicing, all parties must have e-invoicing addresses. This will be the digital destination for the e-invoice and may vary depending on the service provider. Usually in Malaysia, it could be:
- Standard Email Address: Some systems use email addresses to route e-invoices. Businesses can register an email specifically for receiving e-invoices in Malaysia.
- Unique Identifier or ID Number: This is the code issued by the tax authority or e-invoicing service solution provider. In Malaysia, businesses can use identification codes issued by local tax authorities to properly route and authenticate invoices.

Ensuring the standardization of e-invoicing ensures that invoices are sent to the correct recipient and can be processed within the allowed time, without delay.
Formats
The format of e-invoices demonstrates the importance of compatibility and compliance in the process of how does e invoicing work. Some common components usually included in e-invoicing formats are shown below.

XML (Extensible Markup Language) | UBL (Universal Business Language) |
Widely used due to its versatility and compatibility. Malaysian business can tailor XML when used with specific categories, for example:
| Another popular format of e-invoicing. However, it is used more in Europe. This format demonstrates the ability to standardize the structure of business documents. |
Ensuring compliance with the correct format of e-invoices helps you read and process invoices automatically. This minimizes errors and speeds up transactions in the process of how does e-invoicing work.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure for e-invoicing refers to the system and network used to exchange e-invoices between parties. In general, there are 3 types of models when it comes to infrastructure of how does e invoicing work.
- 2-Corner Model: This is a peer-to-peer (P2P) model, in which suppliers and buyers directly exchange electronic documents. E-invoicing is sent using EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) or XML files without intermediaries. It's like a direct message from one computer to another.
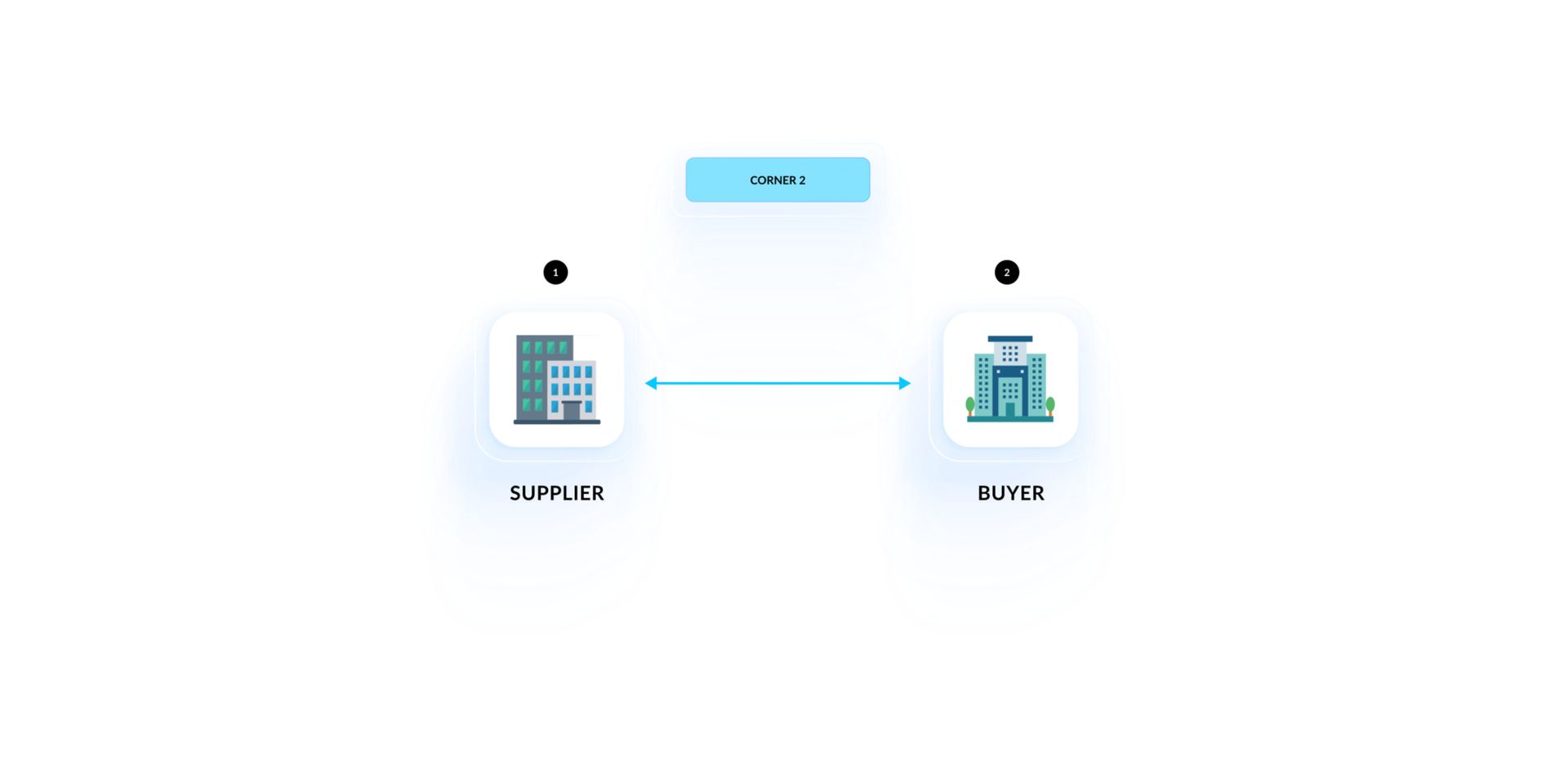
- 3-Corner Model: In this model, both suppliers and buyers use the same third-party service provider to exchange documents. The service provider handles the money transfer process, often using cloud-based solutions or specialized electronic invoice software. This setup simplifies the process because both parties use the same platform to work, minimizing compatibility issues.
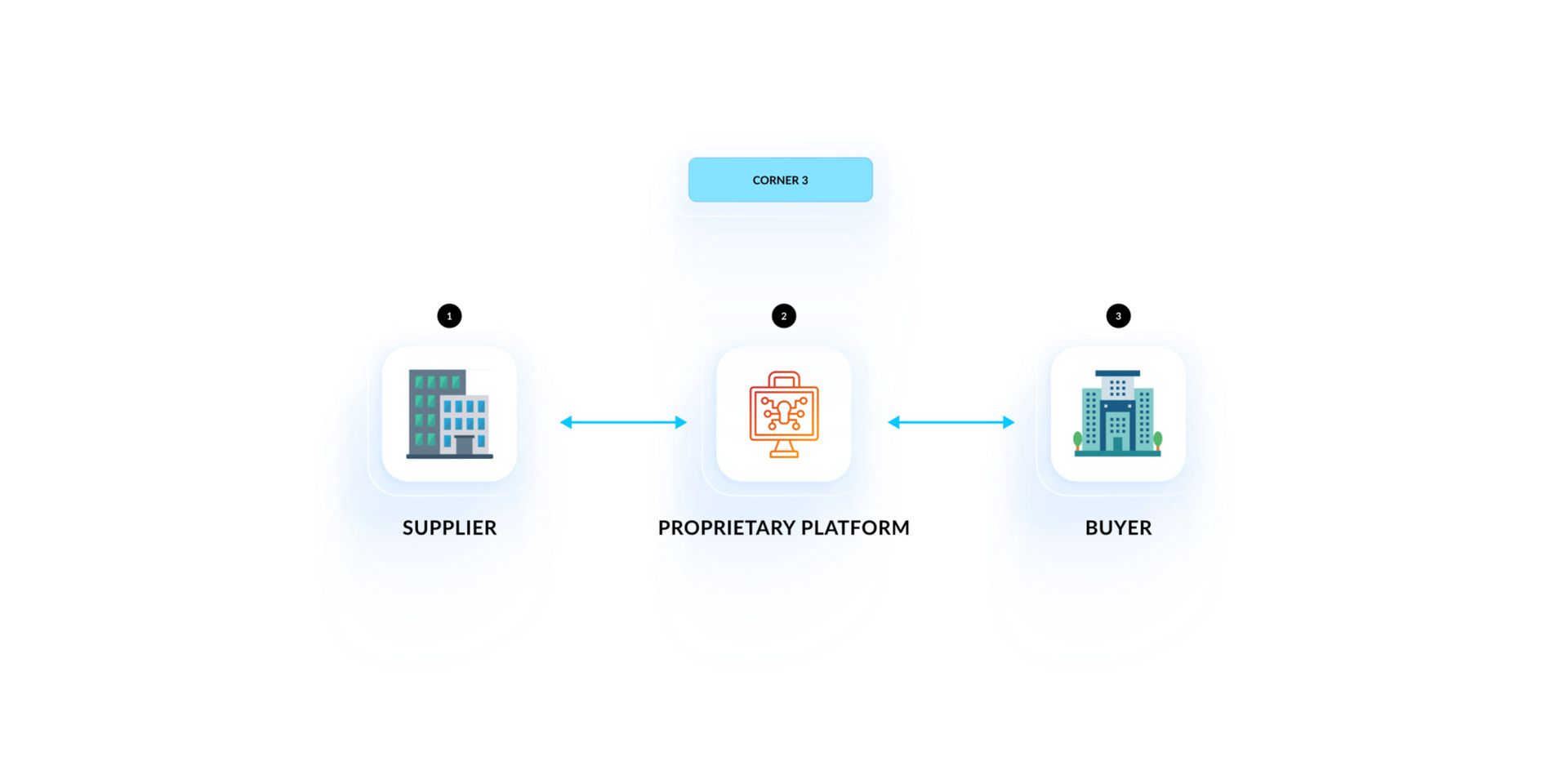
- 4-Corner Model: This model involves both parties using many different service providers to handle the e-invoicing journey and answer smoothly how does e-invoicing work.
For example, a Malaysian supplier may use a local e-invoicing provider, while the buyer in another country uses a different provider. These two providers work together to facilitate the exchange process, ensuring e-invoices are converted and sent in the correct format to each party.

Knowing these 3 parts in detail, Malaysian business owners can better navigate the transition to e-invoicing, master the journey of how does e-invoicing work, and ensure compliance with all legal conditions. the law.
6 Crucial Steps of How Does E-Invoicing Work
Comprehending the steps of how does e-invoicing work helps you be more proactive in streamlining your e-invoicing process. From invoice creation to final validation and integration steps, we will provide a detailed analysis below based on the opinions of experts with extensive experience in implementing e-invoicing projects.
Step 1: Invoice Generation
The process begins when the supplier creates an invoice in a specified electronic format, usually JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). This format includes all the necessary details for both the supplier and the buyer, including invoice number, date, item description, quantity, price, and tax information details.

You can do it using:
- ERP Systems: Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software like Odoo, Tally, or SAP can automatically generate e-invoices. For example, if you are using Odoo, it will be easy for you to generate invoices in JSON format with all the necessary details automatically.
- Offline Utility Tools: Businesses can also use offline tools provided by the Malaysian tax authority to manually enter invoice details and generate JSON files.
Step 2: Real-Time Validation by MyInvois Portal
Once the e-invoice is created, you need to transfer it to MyInvois Portal for validation. As a supplier, you can upload e-invoices to the portal manually or use the API to send them automatically.
MyInvois Portal will perform validation by checking invoices for compliance with formatting standards, and verifying the accuracy of the data provided. It typically involves checking the GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) of both suppliers and buyers, ensuring the invoice date is within the allowable range and confirming the taxable amount is calculated correctly.
The portal will then provide the Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and signature to the e-invoices. The QR code contains the necessary invoice details and an IRN is also generated.
Step 3: Notification of Validated E-Invoice
Once the e-invoice is authenticated, the Inland Revenue Department of Malaysia (IRBM) will notify both parties of the successful authentication. This notification certainly includes both the IRN and the QR code, confirming that the e-invoices have been authenticated and are ready for further use.
Step 4: Sharing of Validated E-Invoice
You share the verified electronic invoice as the next step of how does e-invoicing work with buyers. It has embedded IRN code and QR code, where the QR code contains all the necessary and important information for the invoice.
Ensure that your authenticated e-invoices can be shared through a variety of means, including email, print, or directly integrated into the buyer's accounting system via API.
Step 5: Cancel or Decline E-Invoices (if needed)
Suppliers or buyers have the right to cancel or refuse e-invoices within 72 hours of confirmation. This happens in case there are errors in the invoice or the transaction has been invalidated due to force majeure (from the supplier). Buyers also have the right to refuse if the electronic invoice information does not match the order or goods received.
Cancellation or refusal requests are processed through the MyInvois Portal, ensuring that both parties are thoroughly informed and updated accordingly on the invoice status at any given time.
Step 6: Storage and Access of E-Invoice

Your e-invoice, once authenticated, is stored in MyInvois Portal. This place also maintains its reference in the future. Both suppliers and buyers have access to stored e-invoice records to ensure storage, transparency, as well as easy retrieval for compliance checks and financial reconciliation.
By following these detailed steps, Malaysian businesses can implement e-invoices effectively, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and streamlined operations. This process also reduces the risk of errors or fraud for all businesses, avoiding serious violations of the law.
Standards of E-Invoicing Journey: You Must Fit Which One?
Successfully navigating and applying e-invoicing requires you to understand the different standards used in Malaysia in particular and globally in general (especially for businesses aiming for globalization).
Some typical standards of e-invoices are mentioned below to ensure your e-invoicing journey complies with all conditions and standards related to interoperability and security:
European Standard

The European Commission and EU members have established European Standards on e-invoicing. It is mainly intended for B2G (Business to Government) and G2G (Government to Government) transactions. This standard, outlined in European Directive 2014/55/EU), provides a semantic data model that lists all the essential elements that e-invoices need to comply with.
It supports two XML formats: UBL (Universal Business Language) and CII (Cross Industry Invoice).
Key factors:
- Required invoice information and supplier and buyer details.
- Tax-related information includes VAT numbers.
- Invoice line item with descriptions, quantities, and prices.
- Digital signature for authentication.
Peppol Standard
The Pan-European Public Procurement Online (Peppol) network facilitates the secure exchange of documents between registered users worldwide. To participate, businesses need to go through an access point to Peppol, and ensure all invoices are processed on this framework.
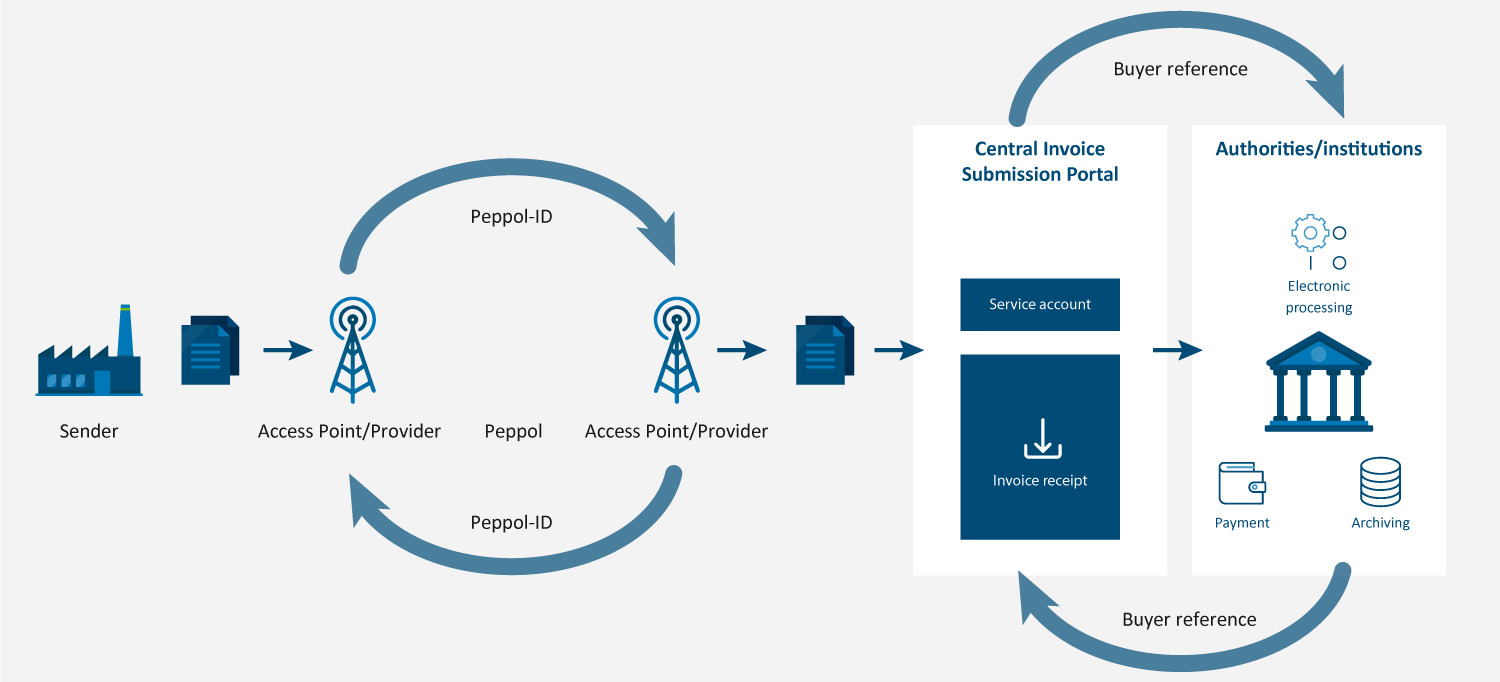
Key factors:
- Standardized document formats.
- Secure, interoperable communication channels.
- Comply with international e-invoicing regulations.
- Centralized authentication and invoice routing.
EDIFACT Standard
The Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport (EDIFACT), established by the United Nations in 1986, is a global set of rules for electronic data exchange through EDI (Electronic Data Interchange). E-invoicing is also included in this process. This widely used standard specifies the address types, formats, and required infrastructure.
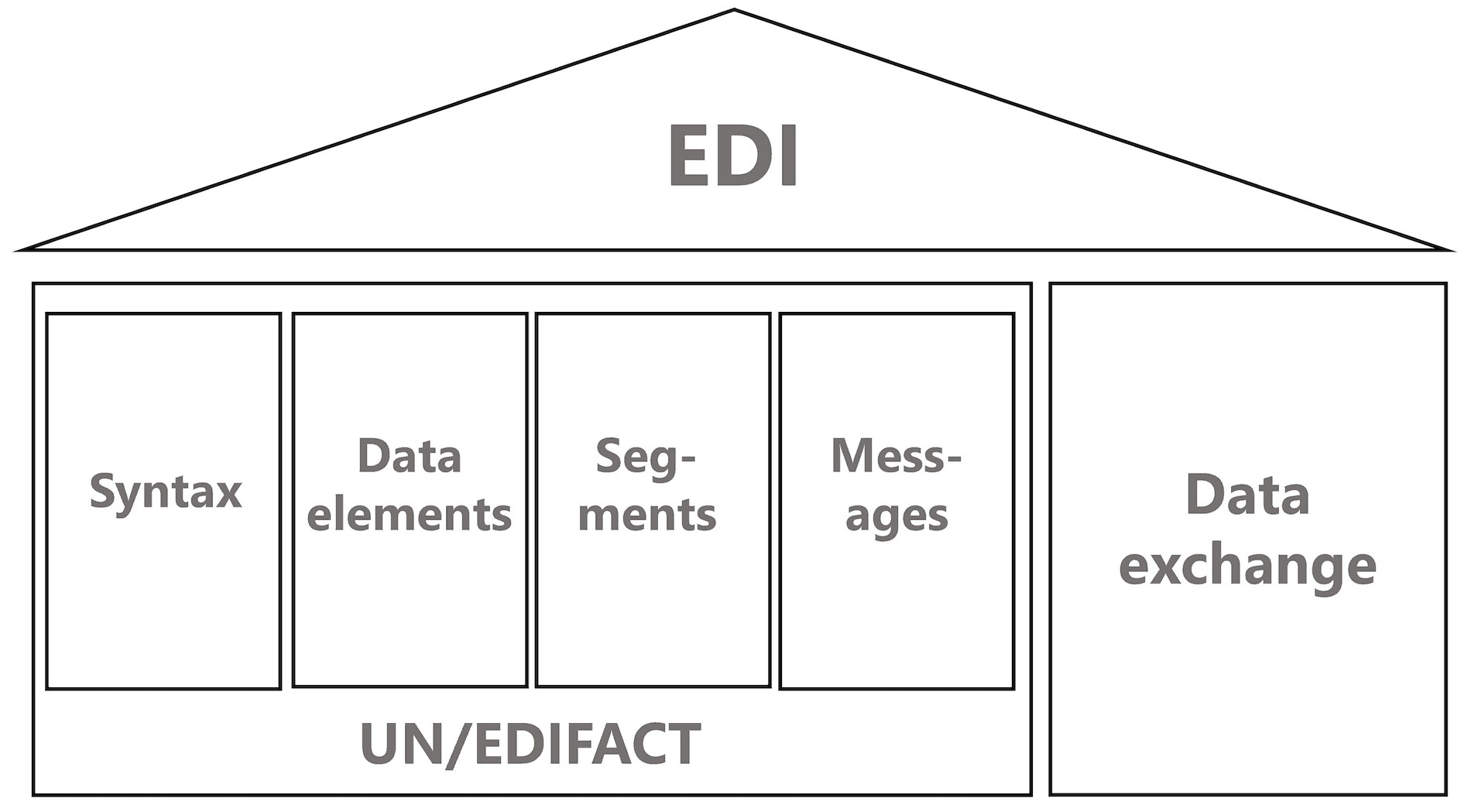
Key factors:
- Standardized messages for different business documents.
- Comprehensive syntax rules for structuring data.
- Security protocols to ensure data integrity and security.
- Ability to support a wide range of business processes.
- Country-specific standards
In addition to international standards, many countries also develop their own e-invoices formats and standards to meet local regulatory and compliance requirements. Some specific examples for your reference (in case you want to scale up in other countries):
- Italian FatturaPA: XML Schema specifically designed to comply with Italian tax law.
- Mexican CFDI: e-invoices format includes digital tax receipts and required fields for tax compliance,
- Nita Fiscal Eletrônica of Brazil: Standardized format for electronic invoices used for all taxable transactions in Brazil.
Each standard has its own set of rules and formats, tailored to meet the legal and business requirements of each respective region. In Malaysia, according to our experience, businesses tend to use Peppol standard.
Understanding which e-invoicing standards need to be applied is important to ensure compliance and smooth business operations. Evaluate your business needs, trading partners as well as your regulatory environment thoroughly to determine it most accurately and effectively.
If this is too complicated and difficult, you should contact e-invoicing experts or your providers so they can give you accurate advice on how does e-invoicing work, and in accordance with your enterprise's development goals.
Make A Good Journey of How Does E-Invoicing Work: Our Best Advice For You
Some key tips that we have learned after many practical e-invoicing projects will help you gain an intuitive understanding of this field. It will also make you more confident when officially applying e-invoicing into practice.
Prepare Your Data Thoroughly
Before proceeding with the process of how does e-invoicing work, make sure all your financial data is accurate and updated in real-time. Ensure all of customer information, product details, and transaction records are entered accurately into your system.
This process minimizes errors and guarantees your e-invoices are accurate from the start.
Integrate Your Systems
Integrate your existing accounting or ERP systems with MyInvois Portal to quickly identify and fix issues with your e-invoices. This process ensures your invoices are less likely to be rejected and speeds up the invoicing process.
Monitor Real-Time Validation
Use MyInvois Portal's real-time authentication feature to find the problem and fix it immediately if one arises. This feedback helps you closely monitor authentication statuses, while saving time, effort, and resources.
Automate Where Possible

Automation can significantly improve the efficiency of the e-invoicing implementation and adoption process. Look for qualified e-invoicing software platforms to automate repetitive tasks like invoice generation, data entry, and validation checks. This process not only saves time but also reduces the possibility of manual tasks, resulting in more accurate and reliable electronic invoices.
Partner with an E-Invoicing Solution Provider
Consider cooperating with reputable e-invoicing providers if you feel your e-invoicing journey has many shortcomings and needs expert support. These vendors provide expertise and resources that help simplify the process of creating and processing e-invoices. They assist with e-invoicing software integration, compliance updates, and provide ongoing support to resolve any issues that may arise.
A1 Consulting, with Odoo e-invoicing and Bizzi digital automation, is as bright a name as your e-invoicing partnership. We confidently enhance your tax administration with our proven portfolio and expert experience.
Final Thoughts
E-invoicing is not a simple journey, and understanding how does e-invoicing work is an important key so that you are not surprised when bringing it into your business. The standards and steps to create accurate, compliant e-invoices will not just be a piece of cake. It is a comprehensive process that requires extreme meticulousness and precision.
If you still have any questions about how does e-invoicing work, as well as want more detailed advice on information related to Malaysian e-invoicing, feel free to get in touch with us and you will be answered thoroughly with custom solutions!
